Tesla Model Y has emerged as one of the world’s best-selling electric vehicles, capturing significant market attention in 2026. Recent strategic moves by Tesla have introduced new pricing tiers and feature configurations that position the Model Y as an increasingly accessible option in the electric vehicle market. This comprehensive analysis examines the various factors contributing to the Model Y’s pricing structure, technological advantages, and overall value proposition in today’s competitive automotive landscape.
Top 20 Key Notes : Tesla MODEL – Y
Table of Content :
- Tesla Model Y – Understanding
- Electric Power – Engine
- Advanced Feature – Technology
- Battery – Energy Management
- Electric Charger – Technology
- Interior User Experience
- Charging Compatibility
- Charging Stations – Global
- Charging Station – USA
- Tire Performance
- Lighting Visibility
- Driving Control
- Accidental Protection
- GPS Navigation
- Car Stereo
- Market Context
- Why this is Cheap?
- Why this is best?
- Avoid Limitations
- Risk Factors
- FAQs
- Conclusion

1
Tesla Model Y Car
Understanding Value Versus Price
While Tesla has introduced more affordable variants of the Model Y, calling it “cheap” misrepresents the vehicle’s actual market position. The newly unveiled Model Y Standard variant is priced at approximately $39,990 in the United States, making it $5,000 less expensive than the previous entry-level Premium Rear-Wheel Drive model. However, this price point still positions the Model Y firmly in the mid-range electric vehicle segment rather than the budget category.
The perception of affordability stems from strategic decontenting rather than fundamental cost reduction. The Standard variant achieves its lower price by removing features including FM/AM radio, the 8-inch second-row touchscreen, adaptive high beams, frequency-dependent shock absorbers, Autosteer function, second-row heated seats, customizable ambient lighting, power-adjustable steering wheel, power-folding mirrors, and first-row seat ventilation.
When comparing the Model Y to competitors in the electric SUV segment, the value equation becomes more nuanced. Traditional luxury features have been stripped away to achieve the lower price point, making it more accurately described as strategically priced rather than genuinely cheap.

2
Engine-Related PROS
The Electric Powertrain Advantage
The Tesla Model Y’s electric powertrain delivers several compelling advantages over traditional internal combustion engines. The absence of a conventional engine eliminates numerous maintenance concerns including oil changes, transmission servicing, spark plug replacements, and exhaust system repairs. This fundamental difference translates into lower long-term ownership costs despite the initial purchase price.
The electric motor configuration provides instant torque delivery, creating a responsive driving experience that conventional engines struggle to match. The Model Y Long Range is rated to accelerate from 0 to 60 mph in 4.8 seconds, though it feels more responsive in real-world driving conditions. This performance level rivals many sports cars while maintaining the practical functionality of a crossover SUV.
The regenerative braking system represents another significant advantage of the electric powertrain. Energy that would typically be lost as heat during braking is instead recaptured and returned to the battery, extending driving range and reducing wear on traditional brake components. This technology not only improves efficiency but also contributes to reduced maintenance requirements over the vehicle’s lifespan.
The simplified mechanical architecture of electric motors inherently requires fewer moving parts than internal combustion engines. This reduction in complexity translates directly to improved reliability and decreased maintenance frequency, creating long-term cost savings that offset the initial purchase price premium associated with electric vehicles.

3
Advanced Features
Technology Integration and Innovation
The centerpiece of this integration is the 15.4-inch touchscreen interface that controls virtually all vehicle functions. This centralized control system receives regular over-the-air software updates, continuously adding new features and improving existing functionality without requiring dealership visits.
The refreshed Model Y incorporates wrap-around ambient lighting, ventilated seats, and invisible speakers that maintain the minimalist aesthetic while delivering premium audio performance. These features demonstrate Tesla’s commitment to combining advanced technology with user-focused design principles.
The vehicle’s Autopilot system represents a significant technological achievement, though it requires careful understanding of its capabilities and limitations. Standard Autopilot features include automatic emergency braking, blind-spot monitoring, lane keep assist, and adaptive cruise control. However, the effectiveness of these systems has evolved significantly over the vehicle’s production history.
Early Model Y vehicles experienced significant phantom braking issues where the car would aggressively brake for oncoming traffic that was safely in the opposite lane, sometimes engaging the ABS system. While these issues have been substantially addressed through software updates, they highlight both the potential and the challenges of camera-based autonomous driving systems.
The integration of entertainment features adds practical value for families and long-distance travelers. The refreshed Model Y includes an 8-inch second-row touchscreen for rear passengers, providing control over climate settings and entertainment options including games and video content. This attention to passenger experience demonstrates Tesla’s holistic approach to vehicle design.
4
Battery Technology
Energy Storage and Management
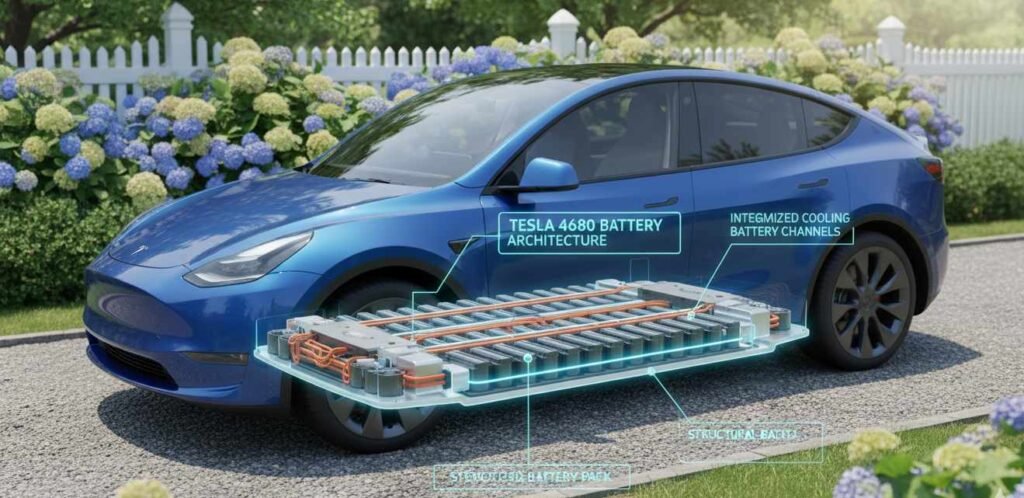
The battery system represents the most critical and expensive component of any electric vehicle, and Tesla’s approach to battery technology significantly influences the Model Y’s value proposition. The Long Range variant utilizes advanced lithium-ion battery technology that balances energy density, longevity, and cost considerations.
Over 25 months of ownership covering 15,410 miles, a Model Y Long Range consumed 4,272 kWh for a total efficiency of 277 Wh/mi, essentially matching the EPA’s official estimate despite significant cold weather operation on snow tires. This real-world efficiency validation demonstrates the reliability of Tesla’s battery management systems and range estimates.
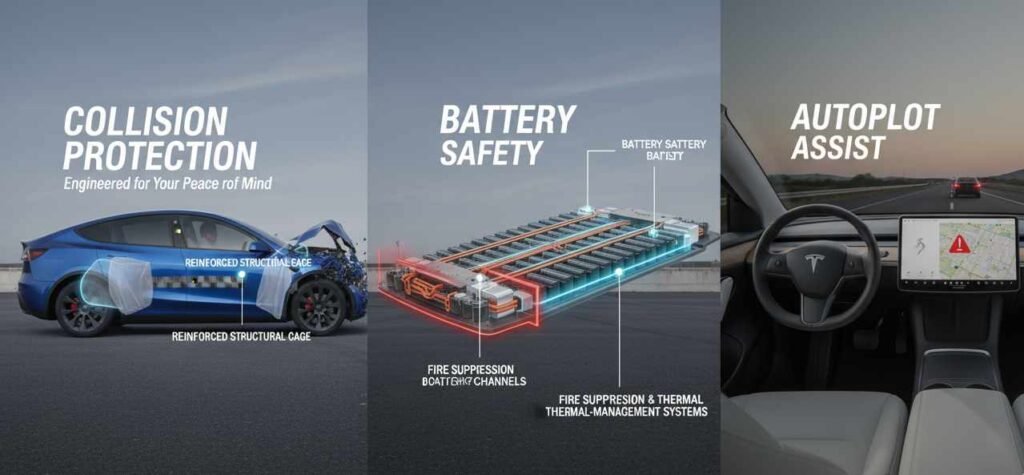
Battery degradation remains a primary concern for electric vehicle buyers, and Tesla’s battery technology addresses this through sophisticated thermal management and charging algorithms. The battery pack utilizes active cooling and heating systems to maintain optimal operating temperatures, which extends battery lifespan and maintains performance across varying environmental conditions.
The structural integration of the battery pack contributes to the vehicle’s overall rigidity and safety performance. By incorporating the battery as a stressed member of the chassis, Tesla achieves both packaging efficiency and enhanced crash protection. This dual-purpose design approach represents an engineering advantage that traditional manufacturers struggle to replicate when adapting existing platforms for electric powertrains.
However, battery-related concerns persist. Some owners have experienced significant range loss while parked, with reports of vehicles losing up to half their charge when left at the airport even after disabling Sentry Mode and other features. These phantom drain issues suggest that battery management systems still require refinement to minimize energy consumption during extended parking periods.

5
Electric Charger
Technology and Compatibility
Tesla’s proprietary charging connector, now standardized as the North American Charging Standard (NACS), represents both an advantage and a potential limitation. All Tesla EVs are equipped with a NACS charging port and require a CCS1-to-NACS charging adapter to use CCS1 chargers. This adapter requirement adds a layer of complexity when utilizing non-Tesla charging infrastructure.
The onboard charging system supports multiple power levels depending on the charging source. For home charging, the Model Y can accept up to 11.5 kW using a Tesla Wall Connector, enabling overnight replenishment from a depleted battery. This level of home charging capability provides practical daily driving convenience for most users without requiring specialized high-power electrical installations.
DC fast charging capability represents one of the Model Y’s most significant practical advantages. The Model Y supports maximum charging power of 250 kW at Tesla Supercharging stations, enabling the vehicle to replenish up to 165 miles of range in approximately 15 minutes. This rapid charging capability fundamentally changes the long-distance travel equation for electric vehicles, making multi-hour road trips practically feasible.
The charging port location on the Model Y has been strategically positioned for optimal Supercharger station ergonomics. Located on the rear driver’s side near the tail light, this placement ensures consistent and convenient cable routing at Tesla’s purpose-built charging stations. However, this location can create awkward cable management challenges at third-party charging stations designed with different port locations in mind.
6
Interior Technology
Cabin Innovation and User Experience
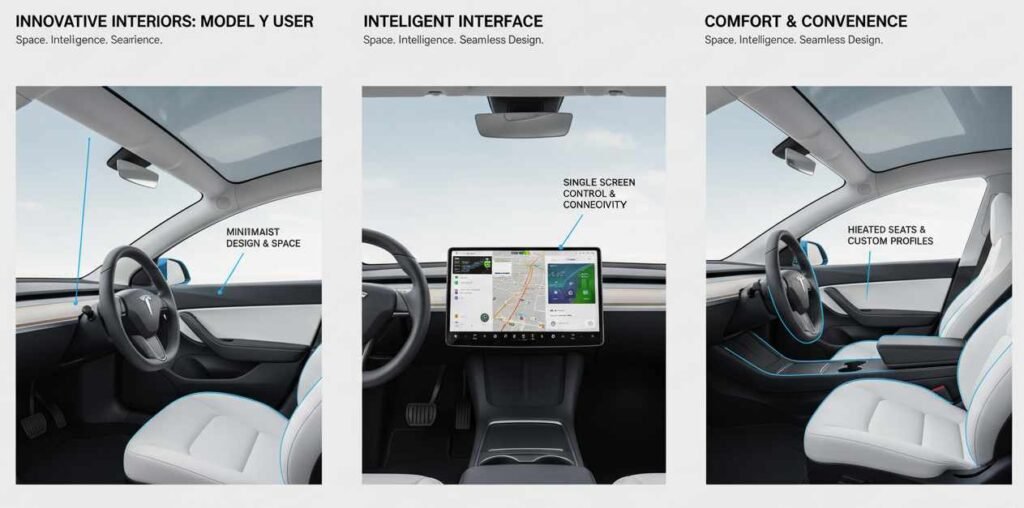
The Model Y’s interior represents a paradigm shift from traditional automotive cabin design. The minimalist approach eliminates virtually all physical buttons and controls, consolidating functions into the central touchscreen interface. This design philosophy divides opinion among users, with some appreciating the clean aesthetic while others find the lack of physical controls frustrating for frequently accessed functions.
The refreshed Model Y features perforated leather upholstery with ventilated seats, a long-requested addition to the model lineup, while retaining the traditional turning stalk unlike its Model 3 sibling. This decision to maintain physical turn signal controls demonstrates Tesla’s willingness to incorporate user feedback rather than pursuing minimalism for its own sake.
The white vinyl interior material, while appearing questionable for a vehicle with luxury pricing, demonstrated remarkable durability over 25 months, showing only minor blue staining from denim that cleaned easily with basic soap. This unexpected durability suggests that Tesla’s material choices balance aesthetics, maintenance requirements, and cost considerations more effectively than initial impressions might suggest.
Climate control represents one area where the touchscreen-centric approach creates practical challenges. Adjusting temperature or fan speed requires navigating through the touchscreen interface rather than reaching for a physical knob or button. The refreshed Model Y addresses some of these concerns with power-actuated first and second-row air vents, providing more precise control over airflow direction.
Storage solutions throughout the cabin reflect thoughtful design considerations. The Model Y offers 2,130+ liters of storage with the power-recline second-row seats folded flat, and the boot automatically unlocks as the driver approaches. This combination of generous cargo capacity and convenient access creates practical advantages for families and active lifestyle users.

7
Electric Charger Compatibility
Universal Access Considerations
The evolution of electric vehicle charging standards has created a complex landscape that the Model Y must navigate. Tesla’s decision to develop and promote the NACS connector as an industry standard represents a strategic move that could simplify future charging infrastructure development. Major automotive manufacturers including Ford, General Motors, and Rivian have announced adoption of the NACS standard for future vehicles.
For current Model Y owners, charging compatibility extends beyond Tesla’s proprietary network through the use of adapters. The CCS1 adapter enables access to the growing network of Electrify America, EVgo, and other third-party charging providers. This expanded compatibility ensures that Model Y owners are not entirely dependent on Tesla’s Supercharger network, though the Supercharger experience generally provides superior convenience and reliability.
Home charging represents the primary energy source for most electric vehicle owners, and the Model Y supports standard 120V household outlets, 240V NEMA outlets, and dedicated Wall Connector installations. The flexibility to charge from various sources provides practical advantages, though charging speeds vary dramatically based on the power source. A standard 120V outlet adds approximately 3 miles of range per hour, while a 240V 50-amp circuit can add up to 30 miles per hour.
The integration of charging scheduling and preconditioning features through the vehicle’s software interface adds practical convenience. Owners can program charging to begin during off-peak electricity rate periods, optimizing energy costs. Additionally, the battery preconditioning function prepares the battery for optimal fast charging performance before arriving at DC fast charging stations, minimizing overall charging time.

8
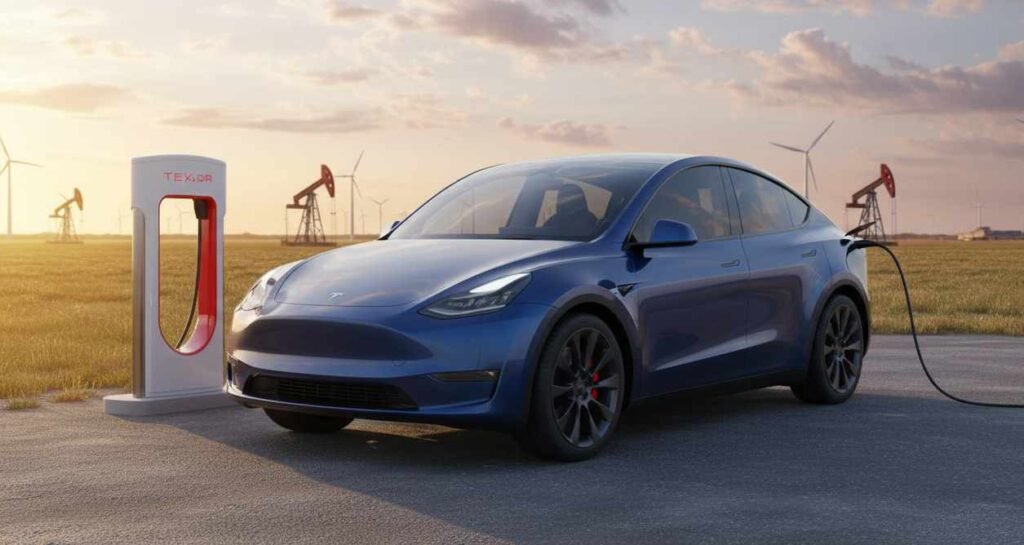
Charging Stations Across the World
Global Infrastructure Focus
Tesla has strategically developed the most comprehensive proprietary charging network in the electric vehicle industry. The Supercharger network has expanded to cover major transportation corridors and urban centers across North America, Europe, Asia, and Australia. This infrastructure investment represents a significant competitive advantage that influences the total cost of Model Y ownership by ensuring reliable long-distance travel capability.

9
Charging Infrastructure in the USA
Strategic Deployment
The United States Supercharger network represents Tesla’s most mature and extensive charging infrastructure deployment. As of January 2025, there are 2,128 Tesla Supercharger locations throughout the United States, with California leading at 426 locations representing 20% of all Supercharger sites nationwide.
Urban charging coverage concentrates in major metropolitan areas where electric vehicle adoption rates are highest. San Diego leads all US cities with 26 Supercharger stations, followed by Las Vegas with 24 stations, with both cities offering 408 charging ports. This concentration reflects both population density and the regional popularity of electric vehicles in these markets.
Major city coverage includes extensive Supercharger deployment in:
- Los Angeles – Multiple locations throughout the metropolitan area serving the nation’s largest Tesla customer base
- San Francisco Bay Area – Dense network coverage supporting high EV adoption rates in Northern California
- New York City – Strategic locations in Manhattan, Brooklyn, and surrounding boroughs
- Chicago – Coverage throughout the metropolitan area and major suburban corridors
- Houston – Extensive network serving the Texas market
- Phoenix – Multiple locations supporting Arizona’s growing EV population
- Seattle – Comprehensive coverage in the Pacific Northwest
- Miami – Network serving South Florida’s coastal communities
- Atlanta – Hub coverage for Southeast regional travel
- Denver – Mountain region access and urban charging
- Boston – Northeast corridor support and urban charging
- Washington DC – Coverage in the nation’s capital and surrounding Virginia and Maryland areas
Interstate highway coverage enables coast-to-coast travel with Supercharger stations strategically positioned along major routes. Early Supercharger deployment enabled travel between Los Angeles, San Francisco, Lake Tahoe, and Las Vegas, followed by Interstate 95 stations in Connecticut and Delaware connecting Boston, New York, and Washington DC. This corridor-focused approach has since expanded to cover virtually all major interstate highways.
The Destination Charging network complements Supercharger locations with slower Level 2 chargers installed at hotels, restaurants, shopping centers, and tourist destinations. While these chargers add range more slowly than Superchargers, they serve travelers who are already planning extended stops at these locations.

10
Tire Technology
Performance and Efficiency Balance
Tire selection for electric vehicles requires balancing multiple competing objectives including rolling resistance, noise characteristics, grip performance, and durability. The Model Y’s standard tire specifications reflect these considerations while attempting to optimize efficiency and range.
The Standard variant features new 18-inch wheel designs as standard equipment, while other Model Y variants offer 19-inch and 20-inch wheel options. The smaller wheel diameter typically provides improved ride comfort and reduced tire cost, while larger wheels enhance handling response and aesthetic appeal at the expense of efficiency and comfort.
Low rolling resistance tires contribute significantly to the Model Y’s impressive efficiency figures, but these tires often compromise grip performance in challenging conditions. On factory all-season tires, the Model Y performed poorly in snow, with the hard, low-rolling-resistance tires providing inadequate traction in winter conditions. This limitation highlights the importance of dedicated winter tire sets for owners in regions with significant snowfall.
After installing studded Nokian Hakkapeliitta 10 EV winter tires, the Model Y transformed into a proper snow performance vehicle, with the softer sidewalls also noticeably improving the vehicle’s generally harsh ride quality. This improvement demonstrates how tire selection can significantly influence overall vehicle character beyond simple grip considerations.
Tire wear rates on electric vehicles generally exceed those of comparable internal combustion vehicles due to increased weight and instant torque delivery. The Model Y’s original tires showed significant wear after just 15,000 miles despite using dedicated snow tires through winter months. This accelerated wear pattern represents a hidden ownership cost that potential buyers should factor into their total cost calculations.

11
Lighting Technology
Visibility and Safety Features
The Model Y’s lighting systems have evolved significantly between model years and trim levels, with recent changes specifically targeting cost reduction in the more affordable variants. The more affordable Model Y spotted testing features removal of the front light bar that was added with the Juniper refresh, reverting to separate headlights. This decontenting represents a visible differentiation between premium and standard models.
At the rear, the signature full-width red light bar has been eliminated and replaced by a horizontal black line without the “T E S L A” badging featured on Juniper refresh models. These lighting changes serve dual purposes of cost reduction and visual differentiation between model tiers, creating a hierarchy that reinforces pricing differences.
Headlight technology in premium Model Y variants utilizes adaptive LED systems that adjust beam patterns based on vehicle speed, steering angle, and oncoming traffic. These systems provide superior nighttime visibility while minimizing glare for other drivers. However, the specific headlight technology included in lower-trim models remains unclear, raising questions about whether adaptive functionality is maintained or replaced with simpler fixed-beam LED systems.
Interior lighting has also received attention in recent model updates. The refreshed Model Y showcases wrap-around ambient lighting with customizable color options, paired with suede-look trim on the doors to elevate the interior’s premium feel. However, these features are absent from the more affordable Standard variant, which eliminates ambient LED lights entirely as part of its cost reduction strategy.
12
Driving Control
Handling and Driver Assistance Systems
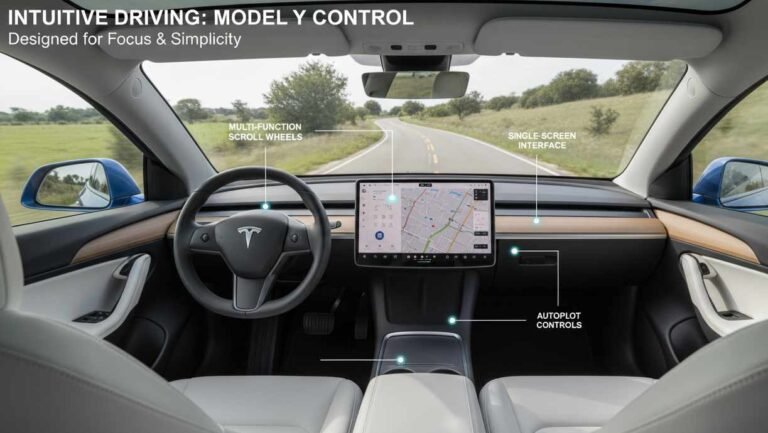
Driving this car present a complex picture that varies significantly based on trim level, tire selection, and road conditions. The steering is described as very quick with minimal feedback, but the speed and small steering wheel diameter create a nimble and engaging feel for an electric vehicle that delivers remarkable efficiency. This characterization suggests a vehicle optimized for efficiency and urban maneuverability rather than traditional driver engagement.
The refreshed Model Y features retuned suspension designed to deliver smoother response and enhanced comfort, with improved steering calibration promising more engaging driver feedback. These updates address one of the most consistent criticisms of earlier Model Y variants, suggesting that Tesla is actively working to refine the driving experience based on customer feedback.
However, suspension quality remains a contentious issue. Even with smaller 19-inch wheels specifically chosen to improve ride quality, the Model Y crashes over every little bump with suspension refinement described as having all the subtlety of a kick in the ass. This harsh ride quality represents a significant compromise that potential buyers must carefully consider, particularly those accustomed to premium luxury vehicles.
The stability control system demonstrates both impressive capability and frustrating limitations. While the system does a respectable job managing available grip, it aggressively intervenes even during intentional spirited driving, killing power at the slightest hint of wheelspin or slip. This conservative calibration prioritizes safety over driving enjoyment, making the Model Y less suitable for enthusiast drivers seeking an engaging dynamic experience.
Winter performance capabilities vary dramatically based on tire selection. With dedicated winter tires, the Model Y becomes a proper monster in the snow, easily handling deep snow conditions, though the stability control system prevents any spirited or sideways driving even on frozen lakes. This limitation again highlights Tesla’s priority of safety over driver engagement.

13
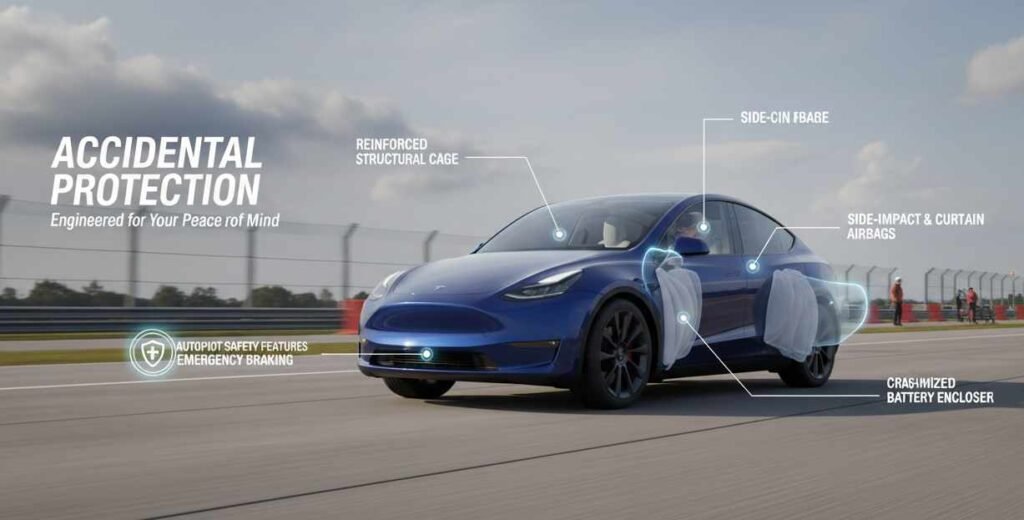
Accidental Protection
Safety Features and Crash Performance
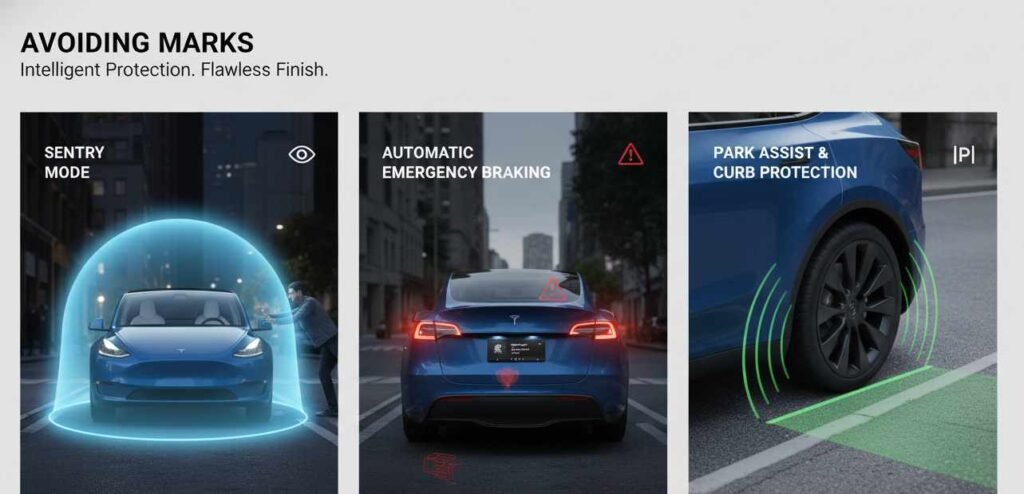
Safety represents one of Tesla’s most emphasized characteristics, with the company consistently highlighting crash test ratings and active safety features. The 2026 Model Y features nine airbags including a new far-side driver airbag, plus an additional forward-facing camera providing improved 180-degree visibility. These enhancements demonstrate Tesla’s ongoing commitment to occupant protection through both passive and active safety systems.
The structural design of electric vehicles provides inherent safety advantages through strategic placement of heavy battery packs and absence of a traditional engine in the front crumple zone. The battery pack’s structural integration into the chassis creates a rigid occupant cell that resists deformation during collisions. This design approach has contributed to the Model Y’s strong performance in standardized crash testing protocols.
Active safety systems in the Model Y include automatic emergency braking that can detect and respond to potential collisions with vehicles, pedestrians, and cyclists. The system utilizes multiple cameras and ultrasonic sensors to monitor the vehicle’s surroundings, though the effectiveness of these camera-based systems has proven variable in real-world conditions.
Early Model Y vehicles experienced frequent phantom braking incidents where the car would stomp on the brakes to avoid oncoming cars that were safely in the opposite lane, sometimes engaging the ABS system. While these incidents primarily represented false positives rather than failures to brake when needed, they created dangerous situations where following vehicles could rear-end the suddenly braking Tesla.
Blind spot monitoring and rear cross-traffic alert provide additional layers of protection during lane changes and parking maneuvers. These systems display visual warnings on the central touchscreen and can provide audible alerts when potential collision risks are detected. However, the reliance on visual notifications through a centralized screen rather than traditional dedicated warning indicators in side mirrors represents a departure from conventional safety interface design.

14
GPS Navigation
Route Planning and Integration
Entire navigation system integrates deeply with the vehicle’s energy management systems to provide route planning that accounts for charging requirements on longer journeys. This integration represents a significant advantage over aftermarket navigation solutions or smartphone apps that cannot access detailed battery state information or predict energy consumption with comparable accuracy.
The navigation interface displays Supercharger locations along planned routes and automatically suggests charging stops when the destination exceeds current range capability. The system calculates arrival state of charge at each charging stop and optimizes total trip time by balancing charging duration against driving time. This optimization can sometimes suggest shorter charging stops at multiple locations rather than fully charging at a single stop.
Real-time traffic integration updates route guidance based on current conditions, with the system capable of dynamically rerouting to avoid delays. The navigation system also integrates with the Autopilot system to enable Navigate on Autopilot functionality, which can automatically execute lane changes and navigate highway interchanges with driver supervision.
However, the navigation system is not without limitations. The Full Self Driving system during testing routinely lingered in the left lane holding up traffic and passed a semi-truck in the right lane, suggesting navigation and lane management logic still requires significant refinement. These behaviors indicate that while the navigation system can plan routes effectively, its integration with autonomous driving features does not always result in socially appropriate or efficient driving behavior.

15
Car Stereo
Audio System Performance
It has 15 speakers and 1 subwoofer, utilizing invisible speaker technology that maintains the minimalist aesthetic while delivering enhanced audio performance. This speaker count compares favorably with luxury vehicle audio systems, suggesting Tesla’s commitment to premium entertainment experiences.
The invisible speaker design integrates drivers throughout the cabin without visible grilles or traditional speaker enclosures, contributing to the clean interior aesthetic. Combined with acoustic glass technology, the audio system creates an optimal listening environment by minimizing road noise intrusion while keeping audio crisp and immersive within the cabin.
Audio sources include traditional options like streaming services through the vehicle’s integrated cellular connectivity, Bluetooth streaming from connected devices, and USB media playback. The large touchscreen interface provides a tablet-like experience for browsing music libraries and controlling playback, though this requires visual attention that traditional tactile audio controls do not demand.
However, the audio system capabilities vary significantly across model tiers. The Standard variant eliminates FM/AM radio entirely as part of its decontenting strategy. This deletion forces owners to rely exclusively on streaming services or personal device content, which may not suit all users’ preferences or work reliably in areas with poor cellular connectivity.

16
Market Analysis
Competitive Positioning and Industry Context
The electric vehicle market has evolved dramatically since the Model Y’s initial introduction, with traditional automotive manufacturers introducing competitive products that challenge Tesla’s early market dominance. This increased competition has fundamentally altered the value proposition and pricing dynamics that the Model Y must navigate.
The absolute cheapest Tesla Model Y starts at $50,490, while the Ford Mustang Mach-E begins at just under $43,000, and the Hyundai Ioniq 5 or Kia EV6 are priced even lower, with all competitors providing driving experiences that are at least as pleasant if not superior. This competitive pressure has forced Tesla to introduce the Standard variant in an attempt to recapture price-sensitive buyers.
The Model Y’s competitive advantages have narrowed considerably as rival manufacturers have developed dedicated electric vehicle platforms. With options like Volvo’s EX30 emerging, plus luxury alternatives including the Audi Q8 E-Tron and Mercedes-Benz EQE SUV available for marginally higher prices, the Model Y’s value proposition has become questionable. In this increasingly competitive landscape, the Model Y primarily distinguishes itself through range performance and the Supercharger network.
Market positioning challenges extend beyond technical specifications to brand perception issues. Over the past two years, owning a Tesla has become a de facto political statement due to the CEO’s public activities, with “many Tesla owners reporting discomfort being seen in their cars” and actively counting months on their leases, canceling pre-orders, or selling their vehicles. This brand perception challenge represents an intangible but significant factor affecting the Model Y’s competitive position.
Sales performance provides mixed signals about the Model Y’s market health. While it remains among the world’s best-selling electric vehicles, growth has slowed as competition has intensified and brand perception issues have emerged. Tesla recently completed its first positive sales quarter in some time, primarily due to expiration of the $7,500 US EV tax credit which pulled forward demand. This dynamic suggests that underlying demand may be softer than headline sales figures initially suggest.

17
Why This Is Cheap?
Cost Reduction Strategies Examined
The introduction of the Model Y Standard variant demonstrates Tesla’s strategic approach to expanding market reach through aggressive decontenting. The budget Model Y lacks the front light bar that normally sits between daytime running lights, with main beams removed from the bumper and integrated into a single headlight assembly. These visible changes signal to potential buyers that the Standard variant represents a fundamentally different product than premium Model Y versions.
Interior feature elimination extends far beyond what casual observers might initially recognize. Firmware analysis reveals the Standard variant lacks a glass roof, features much simpler ambient lighting, eliminates the rear screen, removes power-folding side mirrors, utilizes a fiberglass headliner, and incorporates special motor configurations. The cumulative effect of these deletions creates significant cost savings that enable the lower price point.
Manufacturing efficiency improvements contribute additional cost reductions beyond simple feature deletion. Tesla’s ongoing refinement of production processes, vertical integration strategies, and battery manufacturing scale continue to drive down per-unit costs. These operational improvements enable price reductions without necessarily compromising core vehicle functionality.
However, the cost reduction strategy carries significant risks. The short-lived single-motor Cybertruck provides a cautionary example, as that stripped-down variant cut too many corners while keeping the price tag relatively high, leading Tesla to discontinue the offering. This precedent suggests that finding the optimal balance between cost reduction and customer satisfaction remains challenging.
The question of whether $40,000 represents genuine affordability requires careful consideration. A leaked price of $40,000 for the Standard Model Y would represent a $5,000 savings over the current $45,000 base price, but would still cost $2,500 more than the deal available just before tax credit expiry. This comparison suggests that “affordable” remains a relative term when discussing Tesla pricing.

18
Why This Is Best?
Competitive Advantages Highlighted
Despite intensifying competition and brand perception challenges, the Model Y retains several compelling advantages that support its position as a leading electric vehicle option. The Supercharger network represents the most significant competitive moat, providing convenient and reliable long-distance travel capability that rival manufacturers still struggle to match.
Range performance continues to position the Model Y favorably against most competitors. Tesla estimates the driving range of both the Model 3 and Model Y Standard to be 321 miles on America’s strict EPA test cycle. This range capability exceeds many competitors and addresses the range anxiety that continues to inhibit electric vehicle adoption among potential buyers.
The Model Y demonstrated remarkable reliability with zero mechanical issues over 25 months requiring no service visits. This reliability record, while anecdotal, suggests that Tesla’s electric powertrains have achieved impressive durability when electrical and software issues are excluded. The absence of complex mechanical systems inherent to internal combustion engines contributes to this reliability advantage.
Software capabilities and over-the-air update functionality represent areas where Tesla maintains substantial technological leadership. The ability to add new features, improve performance, and address issues through wireless software updates creates ongoing value that traditional automotive manufacturers struggle to replicate. This software-defined vehicle approach enables continuous improvement throughout the ownership experience.
The direct sales model eliminates traditional dealership markups and negotiation processes, creating pricing transparency that many buyers find refreshing. While this approach generates its own controversies, particularly around dynamic pricing that can feel arbitrary, it does provide a streamlined purchasing experience that removes some of the friction traditionally associated with vehicle acquisition.
19
Avoid the Consequences
Ownership Considerations and Limitations
Prospective Model Y buyers must carefully consider several significant limitations and potential ownership challenges before making purchase decisions. The harsh ride quality represents one of the most consistently reported complaints that can fundamentally affect daily driving satisfaction. Even minor imperfections in asphalt result in painful feedback in the cabin, with the suspension crashing over every little bump despite choosing smaller 19-inch wheels specifically to improve ride quality.
The Full Self Driving system, despite its premium $12,000 price tag, fails to deliver on its ambitious naming. During final testing before lease return, FSD lingered inappropriately in the left lane, passed trucks in the right lane, took exits without using turn signals, swerved wildly between lanes, slowed to 20 mph below the speed limit on gentle curves, and required forceful steering input to override, with the experience compared to riding shotgun with a pimply 15-year-old with a freshly minted learner’s permit. This performance gap between marketing and reality represents a significant concern for buyers considering the expensive option.
Build quality inconsistencies continue to plague Tesla despite years of production experience. A prototype Model Y spotted testing showed a rear trunk lid that did not fit snugly into its designed position, instead encroaching onto the top of the plastic rear fascia with misalignment visible from a considerable distance. While this specific example represents a pre-production vehicle, similar panel alignment issues have affected customer vehicles
20
Any Risk Factor - Critical Concerns for Potential Buyers
Resale & Software Dependency
Several risk factors deserve careful consideration before committing to Model Y ownership. The rapid evolution of electric vehicle technology creates obsolescence risks, as newer models with superior battery technology, charging speeds, and efficiency metrics regularly enter the market. The Model Y’s technology, while competitive today, may feel dated within a few years as the industry advances.
Resale value uncertainty represents a significant financial risk factor. Tesla’s frequent price adjustments create confusion in the used car market, as vehicles purchased at higher prices compete with newer inventory offered at lower prices. This pricing volatility makes it difficult to predict residual values when calculating total ownership costs.
The expiration of federal EV tax credits in the United States has increased the effective price of new Tesla vehicles by $7,500 for US buyers. This change fundamentally alters the value proposition and makes used vehicles or competing brands more attractive for cost-conscious buyers.
Service availability and quality varies dramatically by location. While some regions have well-established Tesla service centers, others require owners to travel significant distances for warranty repairs or routine maintenance. Mobile service can address some issues, but major repairs still require service center visits.
Software dependency creates both opportunities and risks. While over-the-air updates can add features and fix bugs, they can also introduce new problems or remove functionality that owners relied upon. The lack of control over software updates means that vehicle behavior can change without owner consent.
Brand perception challenges continue to evolve based on factors entirely outside vehicle quality or performance. The CEO’s public activities and political engagement have created associations that some buyers find objectionable, potentially affecting both social acceptance and resale values in certain markets.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Is the Tesla Model Y really cheap compared to other electric SUVs?
The Tesla Model Y is not genuinely cheap but rather strategically priced. The new Standard variant starts at $39,990, which is $5,000 less than the previous entry-level model. However, this pricing is achieved through significant feature removal including the front light bar, rear entertainment screen, power-folding mirrors, adaptive high beams, and numerous comfort features. Competitors like the Ford Mustang Mach-E start at $43,000 and the Hyundai Ioniq 5 is priced even lower, making the Model Y competitively positioned but not exceptionally affordable.
Q2: What are the main advantages of the Tesla Model Y’s electric powertrain?
The electric powertrain delivers instant torque with 0-60 mph acceleration in 4.8 seconds for the Long Range model, requires minimal maintenance without oil changes or transmission servicing, features regenerative braking that extends range and reduces brake wear, and provides 321 miles of EPA-estimated range in the Standard variant. The simplified mechanical architecture with fewer moving parts improves long-term reliability compared to internal combustion engines.
Q3: How extensive is Tesla’s charging network in the United States?
Tesla operates 2,128 Supercharger locations throughout the United States as of early 2024, with California leading at 426 locations. Major cities with extensive coverage include San Diego (26 stations), Las Vegas (24 stations), Los Angeles, San Francisco, New York City, Chicago, Houston, Phoenix, Seattle, Miami, Atlanta, Denver, Boston, and Washington DC. The network enables coast-to-coast travel with charging stations strategically positioned along major interstate highways, and the Model Y supports 250 kW maximum charging power for up to 165 miles of range in 15 minutes.
Q4: What are the biggest drawbacks of owning a Tesla Model Y?
The most significant drawbacks include harsh ride quality that crashes over minor road imperfections, the expensive $12,000 Full Self Driving system that performs unreliably and requires constant supervision, potential battery drain during extended parking (up to 50% charge loss reported), build quality inconsistencies including water intrusion in the frunk, and brand perception challenges related to the CEO’s public activities. The touchscreen-centric controls also require visual attention for routine adjustments, and the low-rolling-resistance tires perform poorly in winter conditions without dedicated snow tires.
Q5: Is the Tesla Model Y a good value compared to competitors in 2025?
The Model Y’s value proposition has become questionable as competition has intensified. While it offers competitive range and the best charging network, competitors like the Mustang Mach-E, Hyundai Ioniq 5, Kia EV6, and Volvo EX30 provide similar or superior driving experiences at lower prices. Luxury alternatives including the Audi Q8 E-Tron and Mercedes-Benz EQE SUV are available for only marginally higher prices. The Model Y primarily distinguishes itself through range performance and Supercharger network access rather than overall value or luxury features.
Conclusion
The Tesla Model Y presents a complex value proposition in the increasingly competitive electric vehicle market of 2025-2026. While Tesla has introduced a more affordable Standard variant priced at $39,990, calling it “cheap” misrepresents the reality of significant feature deletions and compromises required to achieve that price point. The Model Y remains competitively priced rather than exceptionally affordable, particularly when compared to rivals offering similar or superior experiences at lower costs.
The vehicle’s strengths remain compelling for certain buyers. The electric powertrain delivers impressive performance with minimal maintenance requirements, the 321-mile EPA range addresses range anxiety concerns, and the Supercharger network provides unmatched long-distance travel capability. Over-the-air software updates and the direct sales model offer advantages that traditional manufacturers struggle to replicate. For buyers who prioritize range, charging infrastructure, and acceleration performance, the Model Y continues to deliver meaningful value.
However, prospective buyers must carefully weigh significant limitations against these advantages. The harsh ride quality represents a daily compromise that affects comfort and satisfaction. The Full Self Driving system, despite its premium price, fails to deliver on its ambitious promises and requires constant supervision. Build quality concerns including water intrusion and panel misalignment persist despite years of production experience. Battery drain during parking and the touchscreen-centric control interface create practical ownership challenges.
The competitive landscape has fundamentally shifted since the Model Y’s introduction. The Ford Mustang Mach-E, Hyundai Ioniq 5, Kia EV6, and emerging options like the Volvo EX30 provide compelling alternatives at similar or lower prices with superior ride quality and traditional luxury features. Premium options from Audi and Mercedes-Benz are available for only marginally higher costs, offering genuine luxury experiences that the Model Y cannot match.
Brand perception challenges represent an intangible but increasingly significant factor in purchase decisions. The CEO’s public activities have made Tesla ownership a political statement for many consumers, with reports of owners feeling uncomfortable in their vehicles and actively seeking alternatives. This association affects both immediate purchase decisions and long-term resale values in ways that are difficult to quantify but impossible to ignore.
-
Final Thought
For buyers who can overlook brand perception issues and tolerate the harsh ride quality, who prioritize range and charging infrastructure above all else, and who value software capabilities and minimalist design philosophy, the Model Y remains a viable option. However, the vehicle no longer represents the revolutionary value proposition it once offered. The electric vehicle market has matured with numerous competitive alternatives that deserve serious consideration.
-
Tips
The ultimate question is not whether the Model Y is cheap, but whether it represents the best value for individual buyers' specific priorities and circumstances. In 2025, that answer increasingly depends on factors beyond technical specifications, encompassing brand perception, driving dynamics preferences, and competitive alternatives that were not available when the Model Y first established its market dominance. Prospective buyers should thoroughly test drive both the Model Y and its competitors while carefully considering total ownership costs, brand associations, and long-term satisfaction before making their final decision.
Technical precision in motorcycles, cars, and automotive gear is established by Nahid Hassan through rigorous evaluation. Performance-driven reviews and high-value affiliate insights are consistently curated at AutoZMotoZ to ensure reader trust. Absolute integrity is maintained in every analysis, with a focus on original and human-verified data.












