Riding a motorcycle is more than just transportation—it’s an exhilarating adventure that offers freedom, thrill, and a sense of accomplishment. For beginners, starting this journey might seem daunting, but with the right guidance and preparation, you’ll be ready to hit the road with confidence. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about how to start riding a motorcycle, from licensing requirements to safety tips and beginner-friendly riding techniques.
Modern motorcycle riding represents an intricate blend of skill development, safety awareness, and technological understanding. This comprehensive guide synthesizes essential knowledge for aspiring riders, incorporating latest industry data and expert insights to create a foundational resource for beginning your motorcycling journey.
Prerequisites: Licensing and Initial Considerations
Why Preparation Matters
When starting your how to start riding a motorcycle the right knowledge and gear ensure a safe and enjoyable experience. Proper preparation helps you avoid common pitfalls, boosts your confidence, and sets the foundation for a lifelong passion.
Licensing Requirements
The Motorcycle Safety Foundation (MSF) reports that properly licensed riders are 37% less likely to be involved in accidents. Before you can ride legally, you’ll need a valid motorcycle license. Here’s how to get started and the key licensing components include:
MSF (Motorcycle Safety Foundation) Courses:
Enrolling in an MSF course is often the best way to learn. These courses cover both theoretical and practical aspects of riding, and many states waive the licensing test if you complete the course.
Age Requirements:
Most regions allow individuals aged 16 and older to apply for a motorcycle permit, though some states may have higher age requirements.
Types of Licenses Available:
- Motorcycle Permit: For learning basic riding skills.
- Motorcycle Endorsement: Added to your existing driver’s license.
- Full Motorcycle License: For those without a regular driver’s license.
Based on country and states the types of license might vary, i.e.:
- Basic Rider Course (BRC): Mandatory in 46 states
- Graduated licensing: Available in select jurisdictions for progressive skill development
Written and Practical Test Requirements:
- Written Test: Tests your knowledge of traffic rules and motorcycle safety.
- Practical Test: Evaluate your ability to control a motorcycle in various scenarios.

Financial Planning
Initial Investment
Initial investment analysis based on current market data:
- Basic training: $200-500 (MSF course)
- Licensing fees: $30-100 (varies by country and state)
- Insurance: $500-1500 annually (comprehensive coverage)
- Essential gear: $1000-2000 (complete safety kit)
- Motorcycle: $4000-8000 (entry-level new or quality used)
Ongoing Maintenance
- Fuel refill
- Engine oil changes
- Tire replacements
- Chain maintenance
- Other regular servicing
New Gear and Performance Upgrade
- Additional new gear will be essential based on the increase in motorcycle usage and experience.
- For performance upgrades, changing the accessories will add some more expenses based on riders’ needs.
Essential Safety Equipment Integration
Primary Protection Systems
Modern motorcycle safety equipment incorporates advanced material technologies and ergonomic design principles when you are learning how to start riding a motorcycle:
Helmet Technology
Current DOT and ECE standards require helmets to meet specific impact resistance metrics:
- Shell composition: Advanced polycarbonate or composite materials
- Impact absorption: Multi-density EPS foam
- Ventilation: Aerodynamically optimized airflow systems
- Visibility: 210-degree peripheral vision minimum
Read Different Types of Motorcycle Helmets with PROS & CONS before choosing the right motorcycle helmet for you.
Protective Apparel
Contemporary riding gear utilizes multi-layer protection systems:
Jackets
- Abrasion resistance: CE Level 2 minimum
- Impact zones: Shoulders, elbows, back
- Material options: Leather (1.2-1.4mm thickness) or textile with equivalent protection rating
Pants
- Hip and knee protection: CE-approved armor
- Abrasion zones: Reinforced seat and knee areas
- Weather adaptation: Waterproof membranes with breathability rating >10,000mm
- Boots
- Ankle protection: Minimum 6-inch height
- Impact resistance: Reinforced toe and heel cups
- Torsional rigidity: Prevents ankle twist during impacts
- Gloves
- Palm protection: Double-layer impact zones
- Knuckle armor: CE-rated impact protection
- Retention: Secure wrist closure systems
Safety Gear
- Armor: Chest protectors and back padding.
- Visibility Equipment: Reflective vests and bright-colored gear.
- Weather Gear: Waterproof and breathable options for rain or heat.
Read more about the >>> Best Motorcycle Accessories a Rider must have here from AutozMotoz article.

Motorcycle Selection Parameters
Beginner-Appropriate Specifications
Statistical analysis indicates optimal starter motorcycle characteristics:
- Engine size: 250-500cc range
- Weight: Below 400 pounds
- Seat height: Allowing both feet flat on ground
- Power delivery: Linear throttle response
- Center of gravity: Low mounting for improved stability
Key Technical Features
Essential systems for new rider safety:
Braking Systems
- ABS (Anti-lock Braking System)
- Combined braking systems
- Emergency brake assist
Engine Management
- Throttle response mapping
- Traction control
- Power modes
Types of Motorcycles for Beginners
- Standard Bikes: Versatile and easy to control.
- Cruisers: Low seats, ideal for relaxed riding.
- Dirt Bikes: Lightweight and great for off-road practice.
- Sport Bikes: Suitable for those looking for speed and agility but require more skill.
While you are learning how to start riding a motorcycle you might be interested in >>> Best Beginner Motorcycle prepared here by the AutozMotoz expters.
New vs. Used Considerations
- New Bikes: Warranty and reliability but higher cost.
- Used Bikes: More affordable, but inspect carefully for wear and tear.
Recommended Starter Bikes
- Honda Rebel 500
- Kawasaki Ninja 400
- Yamaha YZF-R3
However, you may check from the Best Motorcycle Brands – Top 10 in the World for more information.
What to Look for During Inspection
- Tire condition
- Brake functionality
- Chain tension and lubrication
- Fluid levels
Common Beginner-Friendly Features
- Lightweight frame
- Low seat height
- Smooth throttle response
Riding Techniques and Control Operations
Basic Riding Techniques
Practice these fundamental skills in a safe, controlled environment:
- Balancing: Stand over the motorcycle to get a feel for its weight distribution
- Starting from a standstill: Practice using the clutch and throttle smoothly
- Shifting gears: Learn to coordinate clutch and throttle for seamless transitions
- Turning: Practice learning and steering at slow speeds
- Stopping: Master the technique of using both brakes simultaneously
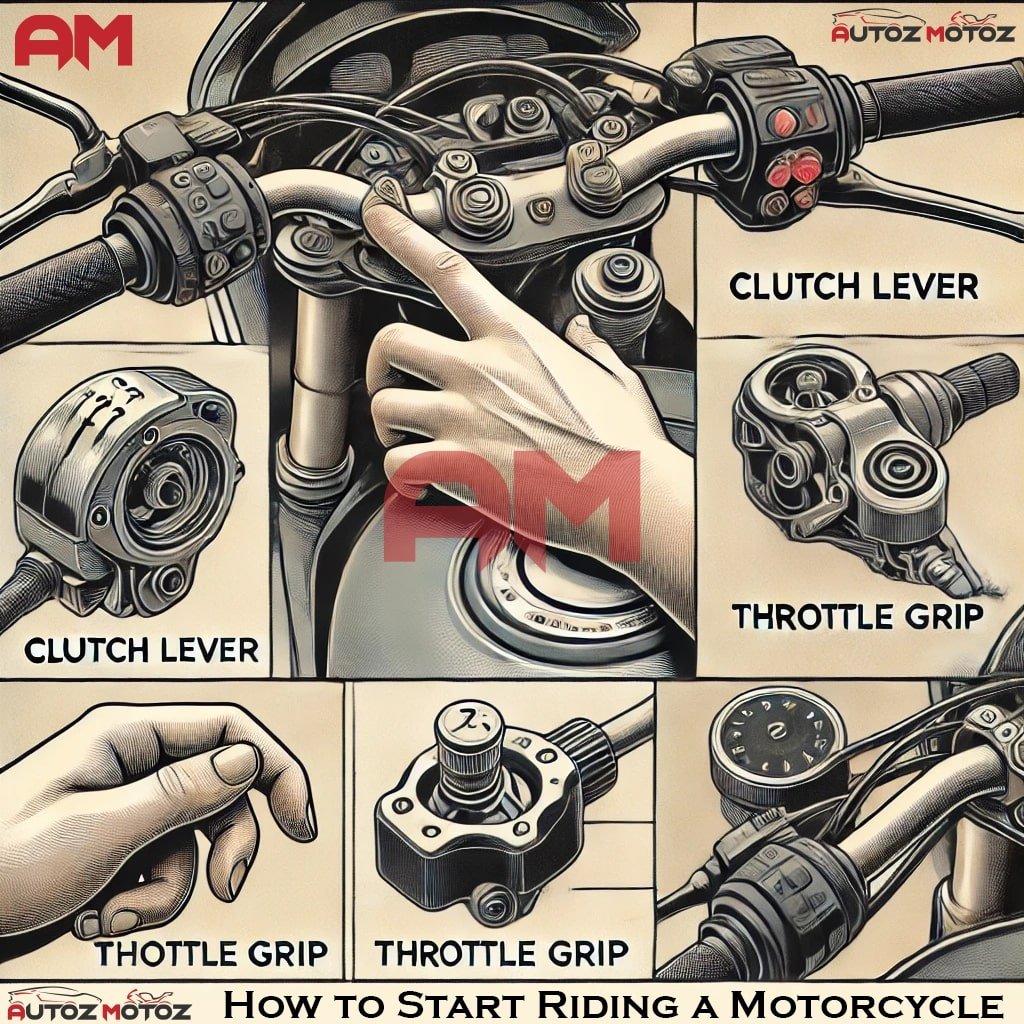
Primary Control Interface
A systematic approach to control familiarization:
Throttle Management
- Quarter-turn sensitivity
- Progressive resistance
- Return spring calibration
Clutch Operation
- Friction zone identification
- Progressive engagement
- Speed-matched shifting
Braking Technique
- Front/rear brake distribution (70/30)
- Progressive application
- Emergency stopping protocols
Secondary Control Interface
- Signals: Indicate your turns.
- Horn: Warns others of your presence.
- Lights: Ensure visibility, especially at night.

Advanced Riding Dynamics
Essential Skill Development
Progressive mastery framework:
Low-Speed Control
- Clutch modulation
- Counterbalancing
- Steering input sensitivity
Cornering Dynamics
- Entry speed management
- Line selection
- Body positioning
- Exit drive optimization
Emergency Maneuvers
- Swerve techniques
- Threshold braking
- Obstacle avoidance
Environmental Adaptation
Weather Considerations
Performance adjustments for varying conditions:
- Rain: Traction reduction of 30-40%
- Cold: Tire temperature management
- Heat: Equipment ventilation requirements
- Wind: Crosswind compensation techniques
Traffic Integration
Strategic positioning for maximum visibility:
- Lane positioning optimization
- Buffer zone maintenance
- Escape route planning
- Visual scanning patterns
Progression Methodology
Skill Development Timeline
Structured advancement phases:
- Basic Operations: 5-10 hours
- Traffic Integration: 20-30 hours
- Advanced Techniques: 50+ hours
Continuous Improvement
Systematic progression markers:
- Smooth control transitions
- Consistent speed management
- Precise line selection
- Automated emergency responses
Building Confidence
- Practice Exercises: Set up a small course in an open area to practice low-speed maneuvers and braking.
- Progression Path: Move from parking lot practice to low-traffic roads before tackling highways.
- When to Upgrade Your Bike: Upgrade when you feel limited by your bike’s performance or features.
- Joining Motorcycle Communities: Join local or online groups to learn from experienced riders and share tips.
Things good to know
Maintenance Basics
Understanding basic maintenance will keep your motorcycle running smoothly:
- Learn how to check oil levels regularly
- Get familiarity with adjusting the clutch and throttle
- How and when to change Engine oil
- Understand and check tire pressure before long ride
- Understand how to change tires when necessary
- Familiarize yourself with common repairs like adjusting brakes or replacing bulbs
Road Safety Tips
As a beginner, it’s essential to prioritize safety:
- Always wear your helmet and other protective gear
- Obey all traffic laws and signs
- Be extra cautious around pedestrians, cars, and other vehicles
- Avoid riding during peak rush hour times or in adverse weather conditions
Group Riding Basics
- Understand group riding signals and indications
- Know full ride plan from the group leader before riding
- Know your position in the group
- Ride in a staggered formation and communicate clearly
Common Beginner Mistakes to Avoid
- Over-revving the engine.
- Forgetting to cancel turn signals.
- Riding beyond your skill level.
Conclusion
Motorcycle riding represents a complex integration of technical skill, safety awareness, and continuous learning. This guide provides fundamental knowledge scaffolding for beginning riders. Regular practice, proper equipment utilization, and ongoing education form the cornerstone of successful motorcycle operation.
Additional Resources
- MSF Advanced Rider Courses
- Local riding groups
- Professional instruction
- Technical workshops
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
When you are planning your first motorcycle and learning how to start riding a motorcycle some common questions that always stand there. Here are the frequently asked questions and their answers from AutozMotoz experts.













One Response